|
在線客服
工作時間 周一至周五 :8:30-17:30 周六至周日 :9:00-17:00 聯系方式 電話:0574-87681087 郵箱:rotic@crystalgenchina.com 地址:寧波市高新區江南路1558 浙大科技園7001室 網址:www.yizhangbing.com 美國公司:25 AUSTIN BLVD,COMMACK,NY 11725 UNITED STATES |
耐藥超級細菌不再無敵 : 撕裂細胞壁的超級藥 | Nature Microbiology 論文推薦 二維碼
548
超級細菌已經成為21世紀對人類健康最大的威脅之一,最近,墨爾本的科學家研發的星形蛋白質分子鏈“結構性納米抗菌聚合肽” (SNAPP)在對抗耐抗生素的超級細菌方面取得了重大突破。SNAPP 通過“撕裂”細菌細胞壁殺死細菌,并毒性較低,進一步深入研究后有望應用于臨床中。 來源 The manufacturer 撰文 Aiden Burgess 翻譯 雷文茜 審校 劉小鷗
正在觀察細菌培養基的研究者。圖片來源:themanufacturer 世界衛生組織指出,能夠對大多數形式的抗生素產生耐受性的超級細菌已經成為嚴重威脅人類健康的殺手。這種耐抗生素超級細菌每年剝奪數百萬人的生命。最近,墨爾本大學工程學院的研究團隊研究出一種名為“結構性納米抗菌聚合肽”(SNAPP)的全新的星形蛋白質分子鏈,可以有效殺死耐抗生素的細菌。相關研究發表于 Nature Microbiology。
研究表明這種聚合肽可以對所有革蘭氏陰性菌,包括 ESKAPE(即腸球菌、金黃葡萄球菌、克雷伯氏菌、不動桿菌屬、假單胞菌屬與腸桿菌生物)和耐粘菌素以及 MDR (CMDR,即多重耐藥)致病菌表現出亞微米級活性,同時具有較低的細胞毒性。
綜合實驗分析表明,SNAPP 的抗菌活性主要以細菌細胞的多模式死亡機制進行,涉及細菌細胞外膜失穩、離子跨細胞質膜運動失調和類凋亡的死亡通路的激活。研究者認為這些機制可能就是 CMDR 細菌沒有對 SNAPP 產生耐受性的原因。
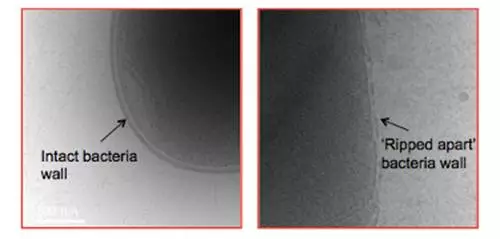
左:完整細菌細胞壁 右:被星形肽聚合物“撕裂”的細胞壁。圖片來源:墨爾本大學 蛋白質分子“撕裂”耐抗生素細菌 這種被叫做聚合肽的星形蛋白質分子鏈通過“撕裂”超級細菌細胞壁的方式殺死它們。 研究者說,正是因為細菌很難適應聚合肽這種“撕裂”細胞壁的方式,所以實驗中沒有發現細菌對聚合肽產生耐受性,這是聚合肽優于抗生素之處。
在探索究竟哪種分子可以突破耐抗生素超級細菌的壁壘的過程中,研究者對六種不同的超級細菌進行了體外測試,最后發現星形聚合肽可以達到這個目標,并且在體外環境中沒有對血紅細胞產生傷害。
研究者也在小鼠體內測試了這種聚合物對一種超級細菌的功效,結果證明聚合肽在實驗中對這種特定的細菌也有效。
不過,研究者認為這項工作仍然處于初級階段,目前只針對一類主要的細菌。未來的研究將會探索其他細菌對這種蛋白質分子的反應。
文章來源 http://www.themanufacturer.com/articles/melbourne-scientists-make-breakthrough-against-antibiotic-resistant-superbugs/ 論文基本信息 【題目】Combatingmultidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria with structurally nanoengineeredantimicrobial peptide polymers【作者】Shu J. Lam. et al. 【刊期】Nature Microbiology 【日期】12. Sep. 2016 【DOI】10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.162 【摘要】With the recent emergenceof reports on resistant Gram-negative ‘superbugs’, infections caused bymultidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacteria have been named as one of themost urgent global health threats due to the lack of effective and biocompatibledrugs. Here, we show that a class of antimicrobial agents, termed ‘structurallynanoengineered antimicrobial peptide polymers’ (SNAPPs) exhibit sub-μM activityagainst all Gram-negative bacteria tested, including ESKAPE andcolistin-resistant and MDR (CMDR) pathogens, while demonstrating low toxicity.SNAPPs are highly effective in combating CMDR Acinetobacter baumanniiinfections in vivo, the first example of a synthetic antimicrobial polymer withCMDR Gram-negative pathogen efficacy. Furthermore, we did not observe anyresistance acquisition by A. baumannii (including the CMDR strain) to SNAPPs.Comprehensive analyses using a range of microscopy and (bio)assay techniquesrevealed that the antimicrobial activity of SNAPPs proceeds via a multimodalmechanism of bacterial cell death by outer membrane destabilization,unregulated ion movement across the cytoplasmic membrane and induction of theapoptotic-like death pathway, possibly accounting for why we did not observeresistance to SNAPPs in CMDR bacteria. Overall, SNAPPs show great promise aslow-cost and effective antimicrobial agents and may represent a weapon incombating the growing threat of MDR Gram-negative bacteria. 【原文鏈接】http://www.nature.com/articles/nmicrobiol2016162 這與我公司產品“超級消毒液"的作用機理很相似,在北美醫院和試驗室很受歡迎,證明了我們的設計理念是很超前的。
文章分類:
行業新聞
|